The Debate Over Plant Milk: Can it Replace Dairy?
Plant-based diets have gained immense popularity, and as a result, plant milk has become a preferred option for many. However, with the increasing interest in veganism, concerns about the health benefits of this milk have arisen. Are they nutritious or just a substitute for “real” milk?
In this blog, we delve into the nutritional content of popular types of plant milk and offer guidance on selecting the healthiest option available. So let’s discover how to make the best decision regarding plant milk and your health.
Types of Plant Milk
Plant-based milk has recently gained much traction if you’re searching for alternatives to cow’s milk. They provide a fantastic alternative for those who are lactose intolerant or want to cut back on animal products in their diet.
Plant-based milk comes from various sources, including nuts, seeds, grains, and legumes. You can conveniently find plant-based milk in stores or make it yourself.
You can choose from wide plant-based milk varieties with distinct flavors and nutritional value. Popular options include almond milk, soy milk, oat milk, coconut milk, and rice milk.
Rice Milk
Rice milk comes from milled rice combined with water before being filtered. It typically has almost no fat content but does include some carbohydrates & proteins, making it beneficial for those looking for something lighter yet still nutritionally beneficial. An 8-ounce glass provides about 5 grams of carbohydrates plus 2 grams each of protein and fiber, essential for a properly functioning digestive system.
Rice milk also offers Vitamin D & B12 and some antioxidants like flavonoids which can help protect against cellular damage caused by free radicals within our bodies – perfect if you want something light yet full of flavor and nutritionally beneficial.
Almond Milk
Almond milk is among today’s most popular plant-based milk due to its creamy texture and subtle sweetness. It’s rich in vitamins E and A, calcium, and iron; it also contains healthy fats such as omega-3 fatty acids to help support heart health.
It is also naturally low in calories and carbohydrates compared to other types of plant-based milk, so it’s an ideal option if you are trying to watch your weight or manage diabetes.
Soy Milk
For centuries, soy milk has been a dietary staple in Asian cultures. Nowadays, it’s increasingly popular among those seeking vegan protein sources, thanks to its ability to provide all the essential amino acids required by the human body.
This milk is made by boiling soybeans, blending them with water, and then straining the mixture through cheesecloth to produce a creamy liquid that resembles cow’s milk. However, it contains much less cholesterol and fat than other animal-based dairy protein sources.
Soy milk is an excellent source of vital nutrients, including B Vitamins, which aid in the efficient breakdown of food into energy, and calcium, which helps maintain strong bones. Consider incorporating soy milk into your diet to reap these benefits.
Oat Milk
Oat milk has gained popularity over the past few years due to its smooth texture and delicious flavor; one cup contains 4 grams of fiber, making it a great way to get your daily dose.
Oat milk is also rich in a variety of vitamins B6, B12 & D which help boost energy levels while providing additional nutrients our body needs, such as magnesium, phosphorus, and zinc – all naturally occurring minerals found within oats.
Oats also contain antioxidant compounds called avenanthramides which help reduce inflammation caused by free radicals in our bodies.
Coconut Milk
Coconut milk comes from the white flesh inside coconuts; it’s thick and creamy with a sweet flavor that makes it perfect for adding richness and creaminess to dishes without any dairy products.
Coconut milk contains essential nutrients such as potassium which helps maintain healthy blood pressure levels by controlling fluid balance within cells. It also contains lauric acid that can help improve cholesterol levels while promoting better digestion thanks to its high fiber content (one cup provides nearly 7 grams).
Finally, coconut milk is a good source of manganese – an essential mineral involved in metabolism & bone formation – making it an important addition when you want something nutritious yet tasty added to your diet.
Nutritional Value of Plant Milk Compared to Cow’s Milk
Plant milk, such as those made from almonds, soybeans, and oats, has become increasingly popular. It’s no surprise that health enthusiasts extol the benefits of plant-based milk; after all, these alternatives are often low-fat and packed with B vitamins and calcium.
But should you cut out cow’s milk entirely? Not necessarily: Dairy products can be a good source of Vitamin D and protein, so adding cow’s milk won’t harm your diet. Ultimately it comes down to personal preference – some people will love the difference that plant milk can make to their eating habits, while others will find that cow’s milk can work well alongside other aspects of their diet.
Whatever you decide to go for – one or the other, or even both – make sure you take note of each one’s nutritional profile and what it could offer you regarding health benefits.
Pros and Cons of Plant Milk
Plant-based milk has been skyrocketing in popularity recently, but before jumping headfirst into the dairy-free train, it pays to weigh the pros and cons.
Pros:
- Nutrient-rich: Plant milk is an excellent source of vitamins and minerals, including calcium, potassium, vitamin A and B complex, zinc, magnesium, and phosphorus.
- Low-calorie & low-fat: Many plant-based milk products have a lower calorie count than dairy milk and are often lower in fat content, making them an excellent option to lose weight or reduce fat intake.
- Easy to digest: As lactose is absent in most plant milk, they are simpler for many individuals to digest. This aspect makes them an excellent alternative to regular dairy milk, especially if you have lactose intolerance.
- Variety in flavor: There is an almost endless variety of plant milk flavors available today, from classic almond milk to more exotic flavors like coconut-almond blend or even macadamia nut milk. This variety means you can easily find plant milk that suits your taste buds and incorporate it into your diet.
- Eco-friendly production: The eco-friendly production of vegan milk makes it a much more environmentally sustainable alternative to regular dairy milk since it doesn’t require the resources to raise cows or maintain farmland. By choosing vegan dairy, you positively impact the planet and contribute to a more sustainable future.
- Versatile uses: Plant milk has diverse applications. Beyond being a beverage, you can incorporate it into recipes for baking and cooking, much like traditional dairy products. Furthermore, it presents the opportunity to craft delectable alternative desserts, including vegan ice cream.
Cons:
- High sugar & salt content: Unfortunately, many store-bought varieties often come preloaded with added sugar and salt for taste, which isn’t healthy if you’re trying to watch your diet closely – opt out of sweetened varieties if possible.
- Allergy triggers: As mentioned before, some plant milk contains nuts such as almonds or macadamias, which could potentially trigger allergies in specific individuals who may be sensitive to them, so it pays to keep this in mind when selecting your product of choice.
- Reduced enzymes & protein content: Regular dairy milk contains enzymes that help break down food faster and proteins that aid muscle growth better than most plant milk products do – so they aren’t always a complete replacement, nutritionally.
- Heavily processed ingredients: Plant milk usually requires more industrial processing than cow’s milk does – meaning that you want to watch for any artificial additives or preservatives when selecting your ideal brand or type of vegan milk.
- Different taste profiles compared to cow’s milk: Plant milk doesn’t usually have the same creaminess or sweetness that traditional cow’s milk has. Adjusting your palate might take some time if you switch from one type of dairy product to another.
- Lower calcium levels than regular Dairy: Regular cow’s or goat’s milk is still a higher source of calcium when compared to most plant-based alternatives. So ensure you get enough vitamins D & K and calcium from other sources (like dark green vegetables) if you regularly consume vegan milk instead.
Conclusion
Plant milk can be tricky, and there’s no 100% consensus on whether it is healthier than traditional animal milk. Soy, coconut, almond, oat, cashew – you name it. They all come with pros and cons that you should consider carefully.
Nutritional value also varies depending on the type of milk and the brands available. Whether plant milk is healthy boils down to your individual needs and preferences, so choose wisely from all the options presented to you.



 Settings
Settings
 Gift Card
Gift Card Blog
Blog Locate Us
Locate Us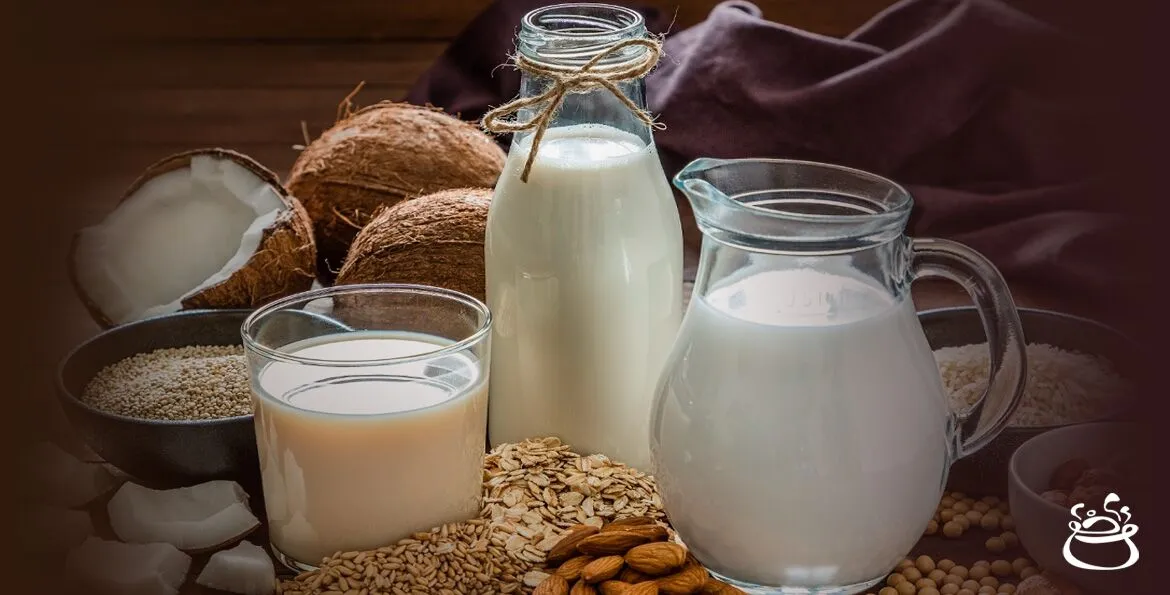








 Home
Home
 Chefs
Chefs
 Chats
Chats
 My Order
My Order



